MySQL CONCAT() AND CONCAT_WS() functions

MySQL CONCAT() function
MySQL CONCAT() function is basically a string function. That means we can use it to do operations on strings. This function is used to concatenate one or more strings. Here, we pass strings as arguments separated by a comma, followed by each string. Thus, it will return a string which will be the result of the concatenation of arguments. The concatenated string will have the same sequence, the arguments were passed.
If any of the arguments passed in CONCAT() function is NULL then it will return NULL. Any numeric argument is automatically converted to its equivalent non-binary string form (1 = ‘1’). If any argument id a binary string then the result will be a binary string otherwise a non-binary string will be returned as result.
Let’s see with examples
/* All arguments are nonbinary strings */
SELECT CONCAT('tech', 'Briefers', '.', 'com') AS result;/* Fourth argument is NULL, other are nonbinary strings */
SELECT CONCAT('tech', 'Briefers', '.', NULL, 'com') AS result;
/* First and second arguments are nonbinary strings and third argument is numeric */
SELECT CONCAT('tech', 'Briefers-', 12345) AS result;
/* First and second arguments are nonbinary strings and third argument is a binary string */
SELECT CONCAT('tech', 'Briefers', 0xaf) AS result;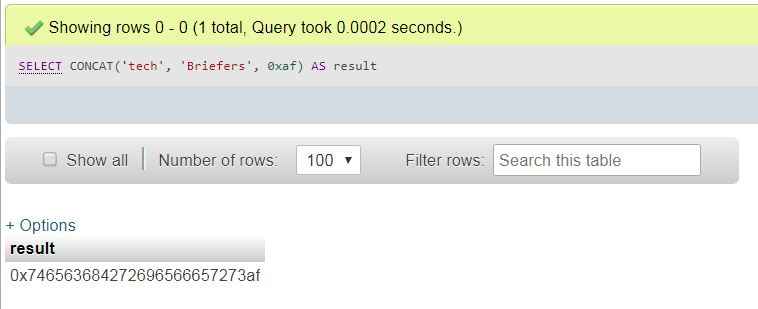
MySQL CONCAT_WS() function
Similarly, MySQL CONCAT_WS() function is also used to do concatenation operations on strings, but with a separator, unlike CONCAT() function. This function concatenates one or more strings passed as arguments with a custom separator. The first argument passed is the separator for all the following strings passed (separated by comma).
This function inserts the separator between two concatenating strings. Hence, the number of occurrences of the separator will 1 less than the number of strings. Eg: Concatenation of – one, two, three with separator – will be ‘one-two-three‘.
If the separator passed in CONCAT_WS() function is NULL then it returns NULL. Otherwise NULL strings are ignored but blank values are not ignored.
Let’s see with examples
/* '-' is the separator for rest of three strings to be concatenated */
SELECT CONCAT_WS('-', 'This', 'is', 'sample', 'string') AS result;
/* NULL is the separator for rest of three strings to be concatenated */
SELECT CONCAT_WS(NULL, 'This', 'is', 'sample', 'string') AS result;
/* '' BLANK is the separator for rest of three strings to be concatenated */
SELECT CONCAT_WS('', 'This', 'is', 'sample', 'string') AS result;
/* ' - ' is the separator and passing blank string */
SELECT CONCAT_WS(' - ', 'This', 'is', '', 'string') AS result;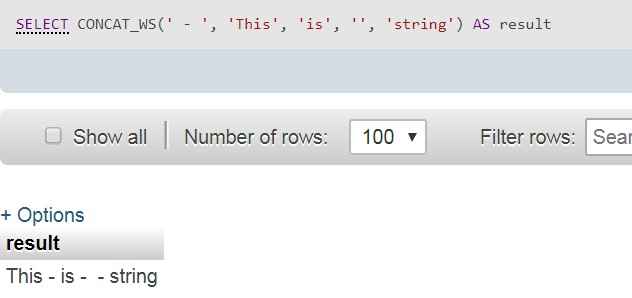
/* '__' is the separator and passing NULL argument */
SELECT CONCAT_WS('__', 'This', 'is', NULL, 'string') AS result;
We can easily concatenate values and strings by using these functions. Below is the example which is a demonstration of the functions in an effective manner.
Click here to Learn SQL.
/* Table structure for table `students` */
CREATE TABLE `students` (
`student_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`student_name` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`student_subject` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`student_grade2` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL,
`student_grade3` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
/* Inserting data for table `students` */
INSERT INTO `students` (`student_id`, `student_name`, `student_subject`, `student_grade2`, `student_grade3`) VALUES
(111, 'John', 'Maths', '20', '30'),
(112, 'Suzan', 'English', '25', '35');Example of CONCAT() function:
SELECT CONCAT(student_id, ' - ', student_name, ' - ', student_subject) AS id_name FROM `students`;
Example of CONCAT_WS() function:
SELECT CONCAT_WS(' - ', student_id, student_name, student_subject) AS id_name FROM `students`








Leave a Reply