What Does COALESCE Do in SQL? Learn with Business Examples

When we work with real sales and marketing data, missing values are unavoidable. A customer may not have a recorded discount, a campaign may not have conversion data yet, or a revenue value may be missing due to tracking issues. This is why understanding what COALESCE does in SQL is so important in data analysis. The COALESCE function helps us handle NULL values safely and produce cleaner, more reliable analytics results.
Instead of allowing NULL values to break calculations or create confusing reports, COALESCE lets us replace missing values with meaningful defaults. This small SQL function plays a big role in professional analytics workflows.
Before going deeper, these beginner-friendly resources help build strong foundations around analytics and SQL:
- What Is Data Analysis? A Complete Beginner’s Guide
- What Is ETL? Extract, Transform, Load with Tools & Process
- SQL for Data Analysis: Queries, Joins, and Real-World Examples
Now, let’s understand COALESCE step by step using realistic business examples.
How COALESCE Works in Simple Terms
COALESCE returns the first non-NULL value from a list of values.
If the first value is NULL, SQL checks the next one. It continues until it finds a non-NULL value.
In simple terms:
- If data is missing, COALESCE provides a fallback
- If data exists, COALESCE leaves it unchanged
This makes analytics queries safer and easier to interpret.
How NULL Values Appear in Sales and Marketing Data
NULL values are common in business datasets.
We often see NULL values in:
- Discount amounts when no discount is applied
- Conversion flags for users who have not converted
- Revenue values for pending transactions
- Campaign metrics for newly launched ads
Without proper handling, these NULL values can cause incorrect results.
Practice Dataset: Marketing Campaign Performance
We will use a digital marketing analytics dataset throughout this article.
How to Create the Sample Table
CREATE TABLE campaign_performance (
campaign_id INT,
impressions INT,
clicks INT,
conversions INT,
revenue DECIMAL(10,2)
);
Explanation:
- campaign_id identifies each campaign
- impressions and clicks track ad visibility and engagement
- Conversions and revenue may contain NULL values
- This structure is common in marketing analytics
How to Insert Sample Data
INSERT INTO campaign_performance VALUES
(1, 10000, 500, 50, 1200.00),
(2, 8000, 300, NULL, 900.00),
(3, 15000, 700, 65, NULL),
(4, 6000, 200, NULL, NULL);
Explanation:
- Some campaigns are missing conversions
- Some campaigns are missing revenue
- These NULL values reflect real-world tracking gaps
This dataset is ideal for practicing COALESCE.
How COALESCE Replaces NULL Values in Query Results
Let’s replace missing conversion values with zero.
SELECT campaign_id,
COALESCE(conversions, 0) AS conversions
FROM campaign_performance;
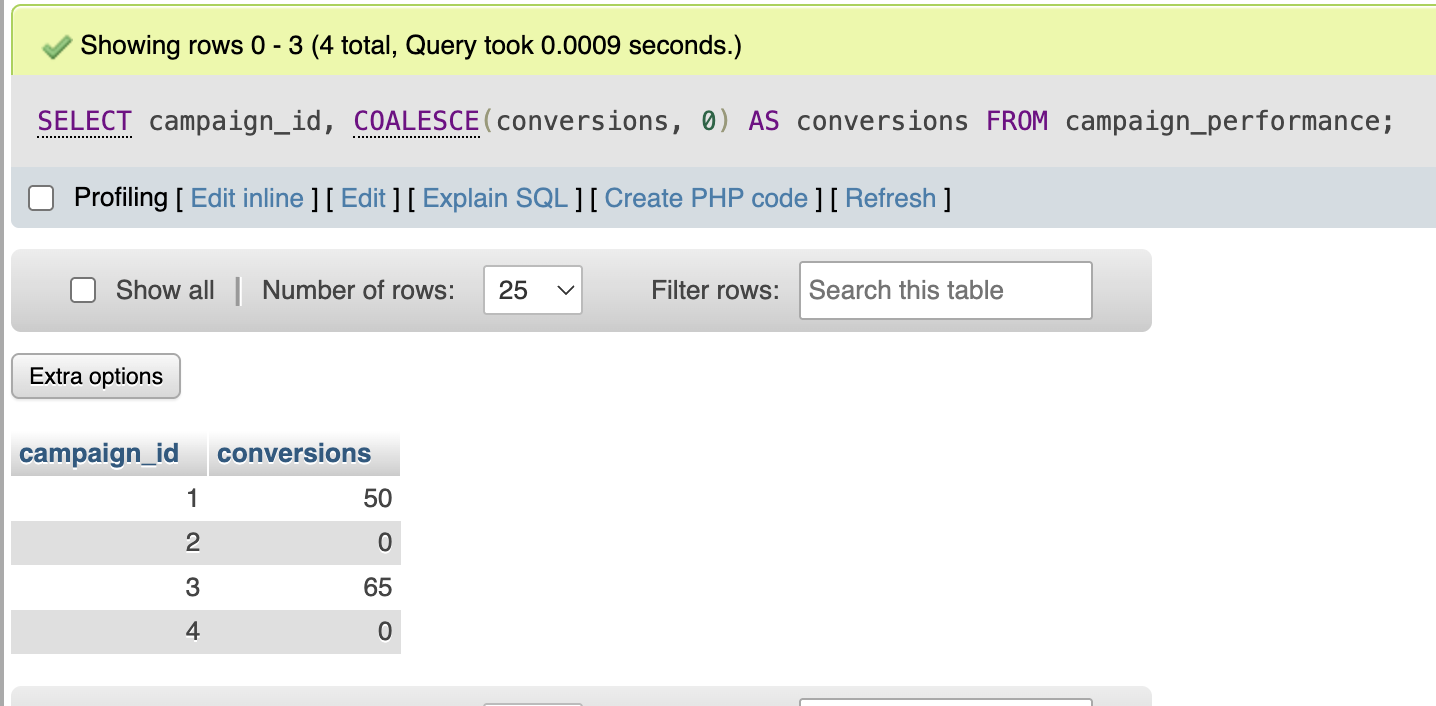
Explanation:
- If conversions is NULL, SQL returns 0
- If conversions exist, SQL keeps the value
- Results become easier to analyze
This is essential for clean reporting.
How COALESCE Prevents Errors in Calculations
NULL values can break calculations if not handled properly.
Example: calculating conversion rate.
SELECT campaign_id,
COALESCE(conversions, 0) * 1.0 / COALESCE(clicks, 0) AS conversion_rate
FROM campaign_performance;
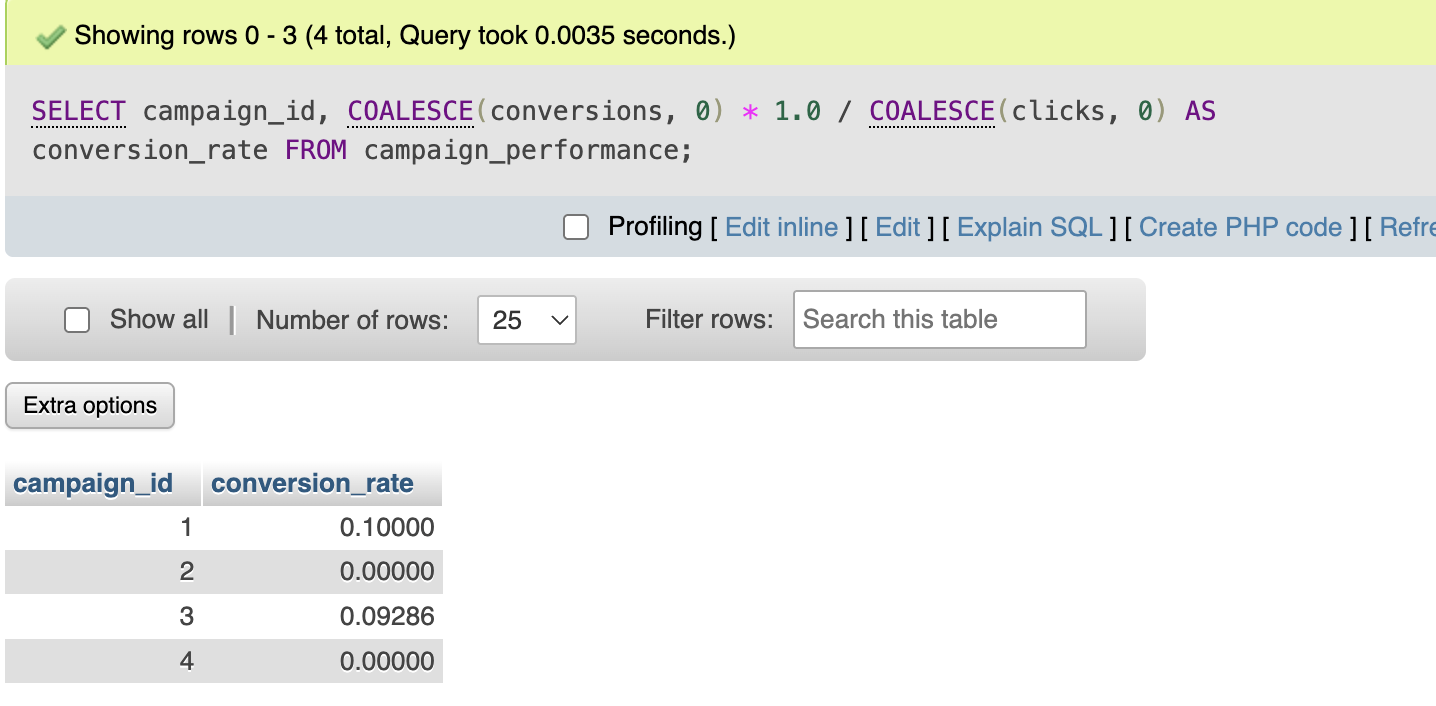
Explanation:
- Missing conversions become zero
- Division works safely
- Results remain meaningful
This prevents unexpected NULL outputs.
How COALESCE Helps in Revenue Analysis
Revenue fields often contain NULL values when transactions are pending.
Example:
SELECT campaign_id,
COALESCE(revenue, 0) AS revenue
FROM campaign_performance;
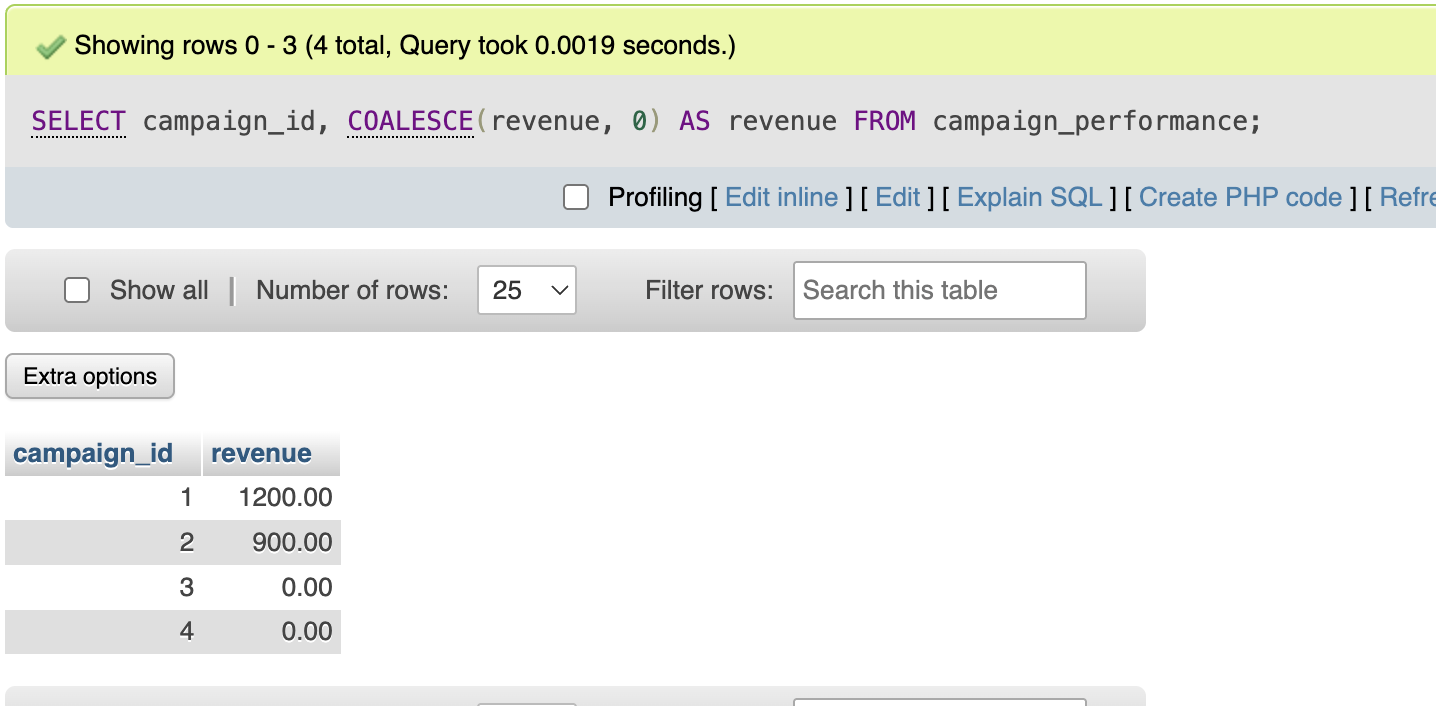
Explanation:
- Missing revenue is treated as zero
- Totals become accurate
- Reports remain consistent
This is common in revenue and pricing analytics.
How COALESCE Works with Multiple Fallback Values
COALESCE can accept more than two values.
Example:
SELECT campaign_id,
COALESCE(revenue, conversions * 20, 0) AS estimated_revenue
FROM campaign_performance;
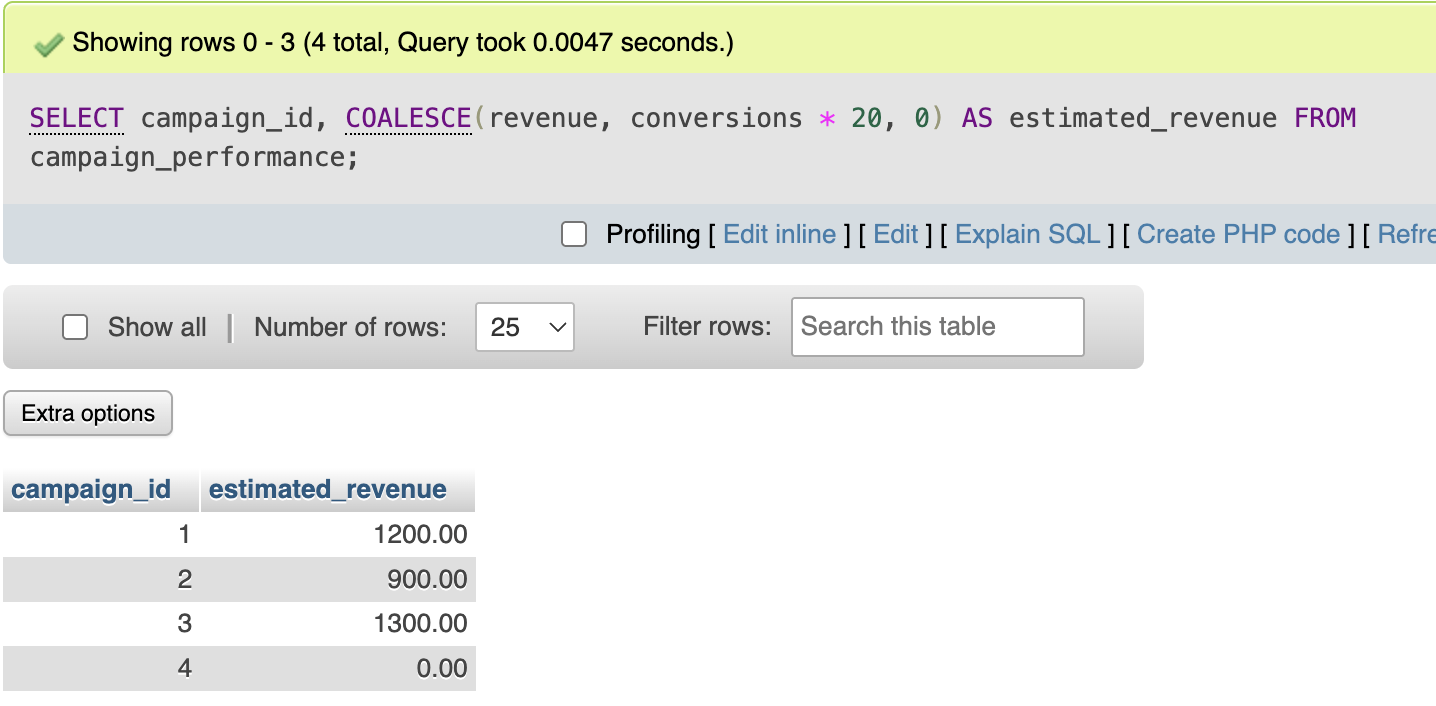
Explanation:
- SQL first checks revenue
- If revenue is NULL, it is estimated using conversions
- If both are NULL, it returns zero
This is useful when working with partial data.
How COALESCE Improves Dashboard Readability
Dashboards often display raw SQL outputs.
Without COALESCE:
- Charts show blank values
- KPIs appear missing
- Stakeholders get confused
With COALESCE:
- Missing values appear as zero
- Metrics look consistent
- Dashboards become easier to understand
This improves trust in analytics.
How COALESCE Fits into ETL and Data Preparation
COALESCE is frequently used during data transformation.
It helps:
- Standardize missing values
- Prepare clean reporting tables
- Prevent NULL-related errors
- Ensure consistent metrics
This makes it a core ETL transformation tool.
How COALESCE Is Different from IFNULL or ISNULL
Some databases offer similar functions.
Key differences:
- COALESCE works across most SQL databases
- It supports multiple fallback values
- It follows SQL standards
Because of this, COALESCE is preferred in cross-platform analytics.
How Beginners Commonly Misuse COALESCE
New analysts sometimes misuse COALESCE.
Common mistakes include:
- Replacing NULLs without understanding business meaning
- Using incorrect default values
- Hiding data quality issues unintentionally
- Applying COALESCE too early in analysis
COALESCE should improve clarity, not hide problems.
How We Should Use COALESCE Thoughtfully
COALESCE is powerful, but it should be used with intent.
We should:
- Choose meaningful default values
- Understand why data is missing
- Document assumptions clearly
- Review metrics after replacement
This ensures responsible data analysis.
Final Thoughts for Freshers in Data Analysis
Understanding what COALESCE does in SQL is a small step that makes a big difference in analytics quality. It helps us handle missing values safely, maintain accurate calculations, and produce cleaner reports.
For anyone learning SQL for data analysis, COALESCE is a must-know function. It is a foundational skill that appears in almost every real-world analytics query.







Leave a Reply